Dix, Rivera y algunos retratos perdidos.
Dix, Rivera and a few lost portraits.
Dix, Rivera and a few lost portraits.
Otto Dix fue otro de los pintores cuyas pinturas fueron tachadas por los nazis de Arte Degenerado. Muchas de sus obras desaparecieron o fueron destruidas, por ejemplo ésta:
Textos en inglés marcados con [*] en cada párrafo.
Otto Dix was another painter whose work was labeled as Degenerate Art by the Nazis. Many of his works disappeared or were destroyed, such as this:
Texts in english at the end of this post, quoted by [*] in each paragraph.
__________________________________________________
Otto Dix
"Kriegskrüppel / Lisiados de guerra / War Cripples"
Según podemos leer en "The Online Otto Dix Project":
"A diferencia de otros trabajos de la muestra, éste evitó la controversia oficial, aunque culpaba claramente a los militares por destrozar toda una generación. Otras en exhibición no tuvieron tanta suerte. Los militares presentaron cargos por insultos contra varios artistas de la exposición.
Cuando Hitler llegó al poder, a Dix se le prohibió exponer su trabajo, mientras que los nazis no sufrieron restricción alguna. En 1933 ésta pintura fue incautada y expuesta en la Exposición de Arte Degenerado de los nazis. Se la tituló «Calumnia contra los héroes alemanes de la Primera Guerra Mundial»" [1a]
Primera feria Dada, Berlín, 1920.
De izquierda a derecha: Hausmann, Höch, Dr. Burchard, Baader, Herzfelde, Margarete Herzfelde, Schmallhausen, Grosz (con sombrero y bastón), Heartfield. La pintura de Dix a la izquierda.
La fotografía se la tomé prestada a Olga ("Totum Revolutum"), de su post sobre Grosz. [1b]
Desconozco el origen de ésta versión coloreada, que incluyo aquí como curiosidad.
I don't know the origin of this colorized version I include here as a curiosity.
Hay también un grabado a punta seca con el mismo motivo:
Here a dry point engraving with the same subject:
"Kriegskrüppel / Lisiados de guerra / War Cripples", grabado, 1920 © VG Bild-Kunst, Bonn 2010
Sin embargo, la obra que me interesaba incluir, y que sufrió la misma suerte que la precedente, es ésta:
However, the work that I wanted to include, and suffered the same fate as the previous one, is this:
"Der Schützengraben / La trinchera / The Trench", óleo sobre lienzo, 227 x 250 cm., 1920-23
"La pintura fue comprada a Karl Nierendorf para el Wallraf-Richartz-Museum en 1923, y más tarde adquirida por el Stadtmuseum and Gemäldegalerie de Dresde. Fue confiscada por los nazis en 1933 y exhibida en la Sala 3 (Inventario Nacionalsocialista Nº 16001) de la Entartete Kunst, la exposición de arte degenerado que tuvo lugar en Münich en 1937 bajo el título "Der Krieg (La guerra)". Se presume que fue destruida.
La compra de "La trinchera" por el Wallraf-Richartz-Museum causó tal protesta que forzó la dimisión de su curador Hans Secker y la devolución de la obra a Nierendorf. En 1924 fue expuesta en la muestra contra la guerra "Nie Wieder Krieg (No más guerra)". La composición y tema de "La trinchera" fue más tarde rehecha como panel central del tríptico de Dix "Der Krieg (La guerra)", que ahora se conserva en la Gemäldegalerie Neue Meister, Dresde." [2]
"Der Krieg / La guerra / The War", óleo sobre lienzo, panel central, 204 x 204 cm., paneles izquierdo y derecho, 204 x 102 cm., inferior, 60 x 204 cm., 1929-32. Gemäldegalerie Neue Meister (Dresde, Alemania).
"Der Krieg / La guerra / The War", óleo sobre lienzo, panel central.
___________________________________________________________
Diego Rivera
En 1931, Diego Rivera conoció a Nelson Rockefeller después que su Museo de Arte Moderno fuera abierto al público, y comenzaron a hablar sobre el proyecto para el Rockefeller Center. Rockefeller estuvo de acuerdo en co-patrocinar el proyecto. El patrocinador original para el mural era la corporación Todd-Robertson-Todd. Decidieron que el mural se instalara en el Gran Hall del Rockefeller Center. Desde esa reunión se alcanzó un acuerdo y se estableció que Rivera continuaría con su trabajo en relación con el capitalismo y el nacimiento del sistema industrial tomando el control de la economía en Estados Unidos. Tras las negociaciones iniciales, Rivera habló con los arquitectos para establecer sus limitaciones. [3]
El mural de Diego Rivera "El hombre en la encrucijada" durante su desarrollo. Mayo de 1933. Edificio RCA, Rockefeller Center, Nueva York. Fotografía: Lucienne Bloch
The mural "Man at the crossroads" during his creation. May, 1933. RCA, Rockefeller Center, New York
Detalle del mural con la imagen de Lenin / Mural detail with Lenin image
El problema principal con el mural de Rockefeller fue la representación de Vladimir Ilyich Lenin. Diego fue obligado a dejar de pintar tras haber completado tan sólo un mes con el mural. El idealismo comunista de Rivera se convirtió en un gran problema legal.
Nelson Rockefeller envió una carta a Rivera: "Me di cuenta de que en la parte más reciente de la pintura había incluido un retrato de Lenin. La pieza está muy bien pintada, pero me parece que este retrato ... podría ofender fácilmente a un gran número de personas .... Por mucho que me disgusta hacerlo, me temo que tenemos que pedirle que sustituya el rostro por el de un hombre desconocido, donde ahora aparece el rostro de Lenin." Rivera se negó, y su contrato se terminó el 9 de mayo de 1933. El mural fue cubierto rápidamente con un lienzo blanco y meses más tarde destruído, el 9 de febrero de 1934. [4a]

Izq. El mural de Rivera, cubierto con tela. Mayo de 1933. Edificio RCA, Rockefeller Center, Nueva York. Fotografía: Lucienne Bloch
Der. Manifestación en el Rockefeller Center en protesta por el cese de Rivera del encargo del mural. 18 de mayo de 1933. Fotografía: New York Daily News [4b]
Pocas horas después de divulgarse el cese de Rivera, una multitud se reúne a las afueras del edificio de la RCA. En los días siguientes, los Rockefeller reciben un alud de cartas de todo el país, algunos alabando el cese de Rivera, otros implorando que se le permita terminar el mural. [4c]

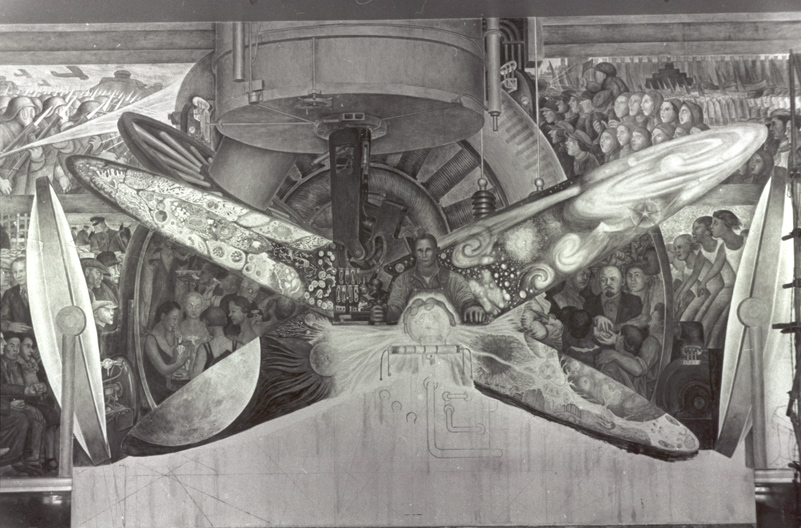
"El hombre, controlador del Universo / Man, Controller of the Universe"
Mural, 4.85 x 11.45 m., 1934. Palacio de Bellas Artes, Ciudad de México.
Una asistente de Rivera, Lucienne Bloch, había tomado fotografías del mural antes de que fuera destruído. Utilizándolas como referencia, Rivera repintó el mural, aunque en una escala más pequeña, en el Palacio de Bellas Artes de Ciudad de México.
_______________________________________________
Es notable el paralelismo entre éstas dos obras y la suerte que corrieron. Ambas fueron absurdamente destruidas por regímenes cuyos valores cuestionaban. Ambas fueron rehechas por sus creadores tras su destrucción y todo ésto prácticamente en los mismos años. [5]
Pero la destrucción deliberada de obras no sólo es cuestión de política, sino también de estética... aún cuando en el caso siguiente ésto tiene mucho que ver con la imagen política del personaje retratado.
But the deliberate destruction of works is not just a matter of politics but also of aesthetics ... even when in the following case this has much to do with the political image of the character portrayed.
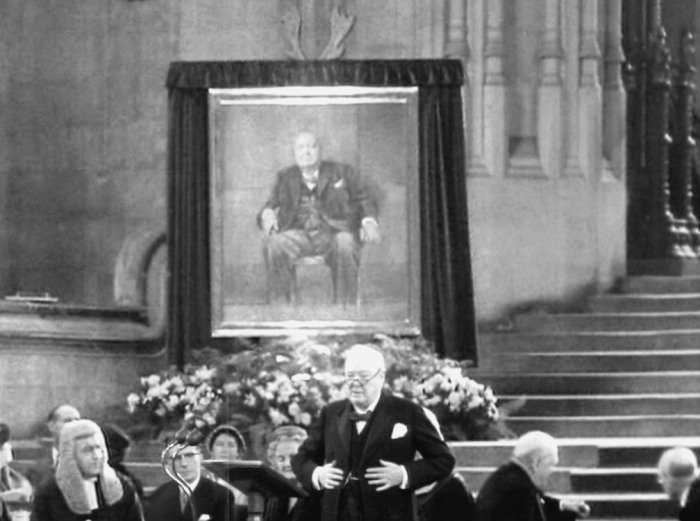
Retrato de Churchill por Graham Sutherland
En 1954, se le encargó a Graham Sutherland que pintara un retrato de cuerpo entero de Sir Winston Churchill. El dinero que se le pagó por la pintura procedía de donaciones de miembros de la Cámara de los Comunes y la Cámara de los Lores, y fue presentada a Churchill por ambas instituciones parlamentarias en una ceremonia pública en el Westminster Hall en su 80 cumpleaños, en noviembre de 1954.
Churchill odiaba el retrato. Tras su presentación pública, la pintura fue llevada a su casa de campo de Chartwell y no se expuso al público. Tras su muerte, la esposa de Churchill destruyó la obra.
Información traducida de Wiki. [6]
Winston Churchill por Graham Sutherland, boceto © National Portrait Gallery, London
Churchill era un anciano estadista en 1954, y estaba finalizando su segundo período como Primer Ministro del Reino Unido. Sutherland tenía una reputación como pintor modernista con algunos retratos exitosos recientes, como el de Somerset Maugham, en 1949. Él se sintió atraído a captar la persona real: algunos sujetos consideraron su falta de inclinación a la adulación como una forma de crueldad o menosprecio. [7]
Churchill ante su retrato recién descubierto durante su presentación en el Westminster Hall, el 30/11/1954
[ver video al final del post / video at the end of this post]
El acto de presentación en el Westminster Hall fue grabado por la BBC. En su discurso de aceptación, Churchill comentó sobre el honor sin precedentes que se le demostraba, y describió la pintura (en un comentario a menudo considerado como un cumplido ambiguo) como "un ejemplo notable de arte moderno", que combina "la fuerza con la franqueza". Otras reacciones fueron variadas, con algunos críticos que elogiaron la fuerza de su semejanza, mientras otros lo condenaron como una desgracia. [8]
Pero tras una larga búsqueda, Freud quedó destrozado al descubrir que la pintura había sido destruída por Breslauer quien se hizo cargo de los negocios de la familia tras la muerte de su padre cuando su piso de Bloomsbury fue destruido durante los ataques alemanes.
El Sr. Breslauer, aparentemente, objetó la forma como Freud había pintado su distintiva papada." [9]
Aunque tal vez el caso más paradigmático en cuanto a destrucción de retratos por parte de los retratados sea el del pintor estadounidense Thomas Eakins. Según podemos leer en el libro de Henry Adams:
"Casi invariablemente los retratos de Eakins fueron pobremente recibidos. Cuatro de los retratos que se le encargaron fueron rechazados. El del Presidente Rutherford Hayes fue destruido. En 1899 los colegas de Dean James W. Holland objetaron su «expresión tensa y casi demacrada» y se negaron a pagar por él. Como explicaron los hijos de Holland, Eakins «no teniendo un mercado por aquél entonces... como gesto de amistad le dimos la pintura a mi madre». En dos casos, los de Robert Ogden y Atwater Lee, los retratados acordaron pagar la factura de Eakins, pero nunca mostraron las obras; uno devolvió el retrato al estudio de Eakins.
Más a menudo, Eakins simplemente entregó los retratos que había pintado al retratado o su familia, a veces acompañados con una descripción adjunta. Muchos nunca se molestaron en recogerlos. Otros destruyeron el regalo. Eakins pintó James y George Wood, los hijos de su médico Dr. Horacito C. Wood, pero ambos retratos desaparecieron. George escribió a Goodrich: "Pintó un retrato mío que era muy "Eakinesiano", tanto que mi familia lo perdió". En 1903 Eakins entregó el retrato de su antiguo alumno Frank W. Stokes a su familia, que lo destruyó. La misma suerte corrió su retrato del boxeador Charlie McKeever, que Eakins entregó a la madre del luchador. John Singer Sargent (o su familia) perdieron o destruyeron el retrato que Eakins hizo de su amigo mutuo Dr. J. William White. De forma similar, la familia Buckley destruyó la obra de Edward S. Buckley que Eakins pintó en 1906. Su hija escribió: "Era tan poco satisfactoria que la destruimos ya que no deseábamos que los descendientes pensaran que su abuelo se parecía a ese retrato." A Mary Waldon, Superiora de la Orden de las Hermanas de la Caridad, no le gustó el retrato que le hizo Eakins y llamó a otro pintor, William Antrim, que pintó uno que le gustó más. Antrim cogió el retrato de Eakins de su bastidor y lo "tiró" en el ático de su estudio, donde al final se perdió." [10]
________________________________________________
Hay otros ejemplos de retratos destruidos por no haber sido del agrado del modelo, por ejemplo el del dramaturgo y novelista Alfred Jarry pintado por Henri Rousseau. No me consta si existen fotografías de ésta obra.
Tampoco de la que Lucian Freud realizó de Bernard Breslauer, un comerciante de libros antiguos. En la noticia, publicada por el Daily Telegraph en agosto de 2008, se puede leer que
"La pintura (...) fue finalizada hace 50 años y Freud estaba muy interesado en que se incluyera en su exposición en Londres el mes que viene.Pero tras una larga búsqueda, Freud quedó destrozado al descubrir que la pintura había sido destruída por Breslauer quien se hizo cargo de los negocios de la familia tras la muerte de su padre cuando su piso de Bloomsbury fue destruido durante los ataques alemanes.
El Sr. Breslauer, aparentemente, objetó la forma como Freud había pintado su distintiva papada." [9]
Aunque tal vez el caso más paradigmático en cuanto a destrucción de retratos por parte de los retratados sea el del pintor estadounidense Thomas Eakins. Según podemos leer en el libro de Henry Adams:
"Casi invariablemente los retratos de Eakins fueron pobremente recibidos. Cuatro de los retratos que se le encargaron fueron rechazados. El del Presidente Rutherford Hayes fue destruido. En 1899 los colegas de Dean James W. Holland objetaron su «expresión tensa y casi demacrada» y se negaron a pagar por él. Como explicaron los hijos de Holland, Eakins «no teniendo un mercado por aquél entonces... como gesto de amistad le dimos la pintura a mi madre». En dos casos, los de Robert Ogden y Atwater Lee, los retratados acordaron pagar la factura de Eakins, pero nunca mostraron las obras; uno devolvió el retrato al estudio de Eakins.
Más a menudo, Eakins simplemente entregó los retratos que había pintado al retratado o su familia, a veces acompañados con una descripción adjunta. Muchos nunca se molestaron en recogerlos. Otros destruyeron el regalo. Eakins pintó James y George Wood, los hijos de su médico Dr. Horacito C. Wood, pero ambos retratos desaparecieron. George escribió a Goodrich: "Pintó un retrato mío que era muy "Eakinesiano", tanto que mi familia lo perdió". En 1903 Eakins entregó el retrato de su antiguo alumno Frank W. Stokes a su familia, que lo destruyó. La misma suerte corrió su retrato del boxeador Charlie McKeever, que Eakins entregó a la madre del luchador. John Singer Sargent (o su familia) perdieron o destruyeron el retrato que Eakins hizo de su amigo mutuo Dr. J. William White. De forma similar, la familia Buckley destruyó la obra de Edward S. Buckley que Eakins pintó en 1906. Su hija escribió: "Era tan poco satisfactoria que la destruimos ya que no deseábamos que los descendientes pensaran que su abuelo se parecía a ese retrato." A Mary Waldon, Superiora de la Orden de las Hermanas de la Caridad, no le gustó el retrato que le hizo Eakins y llamó a otro pintor, William Antrim, que pintó uno que le gustó más. Antrim cogió el retrato de Eakins de su bastidor y lo "tiró" en el ático de su estudio, donde al final se perdió." [10]
________________________________________________
Más sobre Diego Rivera en "El Hurgador" / More about Diego Rivera in this blog:
[Manos a la obra (II)], [Fritz, Frida y el Arte (Fotografía, Pintura)]
Más sobre Diego Rivera en "El Hurgador" / More about Diego Rivera in this blog:
[Manos a la obra (II)], [Fritz, Frida y el Arte (Fotografía, Pintura)]
Otto Dix (Gera, Alemania, 2 de diciembre de 1891 – Singen (Hohentwiel), id, 25 de julio de 1969) fue un pintor de la Nueva Objetividad y el Expresionismo alemanes.
El trabajo pictórico de Otto Dix abarca una gran diversidad de estilos, aunque el gran público conoce, principalmente, sus pinturas sobre la guerra. Dibujante excepcional, Otto Dix nos ha dejado 500 bocetos y diversos retratos, además de lienzos y acuarelas, que, sin duda alguna, evocan la época renacentista. Y es que Dix es, en efecto, uno de los grandes pintores alemanes del siglo XX. La mayor parte de su obra se halla expuesta en el Museo de Arte de Stuttgart. Información de Wiki. In english here.
Graham Vivian Sutherland (Londres, 24 de agosto de 1903 – íd., 17 de febrero de 1980) fue un artista británico nacido en Streatham, Londres. Estudió en Epsom College, Surrey y en el Goldsmith's College de la Universidad de Londres desde 1921 hasta 1926.
No empezó a pintar en serio hasta que tenía treinta y tantos años, después de la caída del mercado del grabado, al que se había dedicado. Sus obras son principalmente paisajes, que muestran una afinidad con la obra de Paul Nash. Sutherland se centra en la inherente extrañeza de las formas naturales, y abstraerlas, a veces dando a su obra una apariencia surrealista; en 1936 expuso en la Exposición Surrealista Internacional de Londres.
Desde 1940 Sutherland fue contratado como artista oficial en la Segunda Guerra Mundial como parte del proyecto de artistas de guerra. Trabajó en el frente doméstico, representando las minas, la industria, y los daños de los bombardeos.
Se convirtió al catolismo en 1926, y desde alrededor de 1950, hasta su muerte estuvo profundamente implicado en la religión. Después de la guerra produjo varias obras religiosas, incluyendo una Crucifixión (1946) para la iglesia de san Mateo, Northampton y el tapiz Cristo en la gloria (1962) para la catedral de Coventry. También siguió produciendo obras basadas en formas naturales, y consiguió fundir parte de ellas -como por ejemplo las espinas- en su obra religiosa. Desde 1947 hasta los años 1960 su obra se inspiró en el sur de Francia, y adquirió una villa en Menton en 1955. Información de Wiki. In english here.
________________________________________________
FUENTES / SOURCES:
[1] - Ficha de la obra en / Artwork record inThe Online Otto Dix Project.
[2] - Texto que acompaña una imagen de la obra en / Text with an image of the artwork inflickr.
[3], [4] - De un artículo sobre el mural en el sitio web de / From an article about the mural in the website of University of Michigan.
[4b], [4c] - Cronología de Diego Rivera / Diego Rivera Chronology, MoMA website.
[6], [7], [8] - Versión en inglés de / English version of Wiki.
[9] - Artículo publicado en / Article published inThe Daily Telegraph, 26 Aug 2008
[11] - Traducido de la versión online en google books de / From the online version in google books of "Eakins Revealed: The Secret Life of an American Artist (Eakins revelado: La vida secreta de un artista estadounidense"
[9] - Artículo publicado en / Article published inThe Daily Telegraph, 26 Aug 2008
[11] - Traducido de la versión online en google books de / From the online version in google books of "Eakins Revealed: The Secret Life of an American Artist (Eakins revelado: La vida secreta de un artista estadounidense"
[1a]
As we can read in "The Online Otto Dix Project":
Unlike many works on display, this one avoided official controversy although it clearly blamed the military for butchering a generation. Others on display were not as fortunate. The military filed charges of insult against several artists at the exhibition.
When Hitler rose to power, Dix was forbidden to exhibit his work but Nazis were under no such restriction. In 1933, this painting was siezed and displayed in the Nazi's Degenerate Art exhibition. It was captioned, "Slander against the German Heroes of the World War."
[1b]
First Dada Fair in Berlin, 1920
From left to right: Hausmann, Höch, Dr. Burchard, Baader, Herzfelde, Margarete Herzfelde, Schmallhausen, Grosz (with hat and cane), Heartfield.
Photograph form Olga's "Totum Revolutum" blog, in her post about Grosz.
[2]
The painting was purchased from Karl Nierendorf by the Wallraf-Richartz-Museum in 1923, and later acquired by the Stadtmuseum and Gemäldegalerie, Dresden. It was confiscated by Nazis in 1933, and exhibited in Room 3 (National Socialist inventory number 16001) of the Entartete Kunst exhibition of degenerate art held in Munich in 1937 under the title Der Krieg (The War). It is presumed to have been destroyed.
The purchase of The Trench by the Wallraf-Richartz-Museum caused such an outcry that it forced the resignation of the museum's curator Hans Secker, and the return of the painting to Nierendorf. In 1924 it was exhibited in the anti-war exhibition, Nie Wieder Krieg (No More War). The composition and theme of The Trench would later be reworked as the central panel of Dix's triptych, Die Krieg (The War), now in the Gemäldegalerie Neue Meister, Dresden.
The purchase of The Trench by the Wallraf-Richartz-Museum caused such an outcry that it forced the resignation of the museum's curator Hans Secker, and the return of the painting to Nierendorf. In 1924 it was exhibited in the anti-war exhibition, Nie Wieder Krieg (No More War). The composition and theme of The Trench would later be reworked as the central panel of Dix's triptych, Die Krieg (The War), now in the Gemäldegalerie Neue Meister, Dresden.
[3]
In 1931, Diego Rivera met Nelson Rockefeller after his Museum of Modern Art opened to the public and began talking about a prospective project for the Rockefeller Center. Rockefeller agreed to be a co-sponsor for the project.
The true benefactor of the mural was the Todd-Robertson-Todd Corporation. They decided to place the mural in the “Great Hall” of the Rockefeller Center. From that meeting they reached an agreement and Rivera was set to continue his work regarding capitalism and the rising industrial system taking control of the economy in America. After initial negotiations, Rivera then talked to the architects to establish his limitations.
[4a]
The main problem with the Rockefeller mural was the depiction of Vladimir Ilych Lenin. Diego was forced to stop painting, after only working a complete month on the mural. Rivera’s communist idealism came to be a very huge legal problem.
Nelson Rockefeller sent a letter to Rivera: “I noticed that in the most recent portion of the painting you had included a portrait of Lenin. The piece is beautifully painted, but it seems to me that this portrait…might very easily offend a great many people…. As much as I dislike to do so, I am afraid we must ask you to substitute the face of some unknown man where Lenin’s face now appears.” Rivera refused, and his contract was terminated on May 9, 1933. The mural was quickly covered with a white canvas. Months later the Rockefellers had the mural hammered off the walls on February 9, 1934.
[4b]
Left. Rivera's Man at the Crossroads covered with canvas. May 1933. RCA building, Rockefeller Center, New York. Photograph by Lucienne Bloch
Right. Demonstration at Rockefeller Center in protest of Rivera's dismissal from the mural commission. May 18, 1933. Photograph by New York Daily News
[4c]
Within hours of learning about Rivera's cease-to-work order, a crowd of protesters gathers outside the RCA building. In coming days, the Rockefellers receive a flood of letters from across the country, some commending Rivera's dismissal, others pleading that he be allowed to finish the mural.
[5]
An assistant, Lucienne Bloch, had taken photographs of the mural before it was destroyed. Using them as a reference, Rivera repainted the mural, though at a smaller scale, at the Palacio de Bellas Artes in Mexico City where it was renamed Man, Controller of the Universe.
______________________________________
There are remarkable parallels between these two works and fate. Both were absurdly destroyed by regimes whose values questioned. Both were rebuilt by its creators after all this destruction and almost in the same years.
[6]
In 1954, Graham Sutherland was commissioned to paint a full-length portrait of Sir Winston Churchill. The 1,000 guineas fee for the painting was funded by donations from members of the House of Commons and House of Lords, and was presented to Churchill by both Houses of Parliament at a public ceremony in Westminster Hall on his 80th birthday on 30 November 1954.
Churchill hated the portrait. After the public presentation, the painting was taken to his country home at Chartwell but was not put on display. After the death of Lady Churchill in 1977, it became clear that she had destroyed the painting some months after it was delivered.
[7]
The true benefactor of the mural was the Todd-Robertson-Todd Corporation. They decided to place the mural in the “Great Hall” of the Rockefeller Center. From that meeting they reached an agreement and Rivera was set to continue his work regarding capitalism and the rising industrial system taking control of the economy in America. After initial negotiations, Rivera then talked to the architects to establish his limitations.
[4a]
The main problem with the Rockefeller mural was the depiction of Vladimir Ilych Lenin. Diego was forced to stop painting, after only working a complete month on the mural. Rivera’s communist idealism came to be a very huge legal problem.
Nelson Rockefeller sent a letter to Rivera: “I noticed that in the most recent portion of the painting you had included a portrait of Lenin. The piece is beautifully painted, but it seems to me that this portrait…might very easily offend a great many people…. As much as I dislike to do so, I am afraid we must ask you to substitute the face of some unknown man where Lenin’s face now appears.” Rivera refused, and his contract was terminated on May 9, 1933. The mural was quickly covered with a white canvas. Months later the Rockefellers had the mural hammered off the walls on February 9, 1934.
[4b]
Left. Rivera's Man at the Crossroads covered with canvas. May 1933. RCA building, Rockefeller Center, New York. Photograph by Lucienne Bloch
Right. Demonstration at Rockefeller Center in protest of Rivera's dismissal from the mural commission. May 18, 1933. Photograph by New York Daily News
[4c]
Within hours of learning about Rivera's cease-to-work order, a crowd of protesters gathers outside the RCA building. In coming days, the Rockefellers receive a flood of letters from across the country, some commending Rivera's dismissal, others pleading that he be allowed to finish the mural.
[5]
An assistant, Lucienne Bloch, had taken photographs of the mural before it was destroyed. Using them as a reference, Rivera repainted the mural, though at a smaller scale, at the Palacio de Bellas Artes in Mexico City where it was renamed Man, Controller of the Universe.
______________________________________
There are remarkable parallels between these two works and fate. Both were absurdly destroyed by regimes whose values questioned. Both were rebuilt by its creators after all this destruction and almost in the same years.
[6]
In 1954, Graham Sutherland was commissioned to paint a full-length portrait of Sir Winston Churchill. The 1,000 guineas fee for the painting was funded by donations from members of the House of Commons and House of Lords, and was presented to Churchill by both Houses of Parliament at a public ceremony in Westminster Hall on his 80th birthday on 30 November 1954.
Churchill hated the portrait. After the public presentation, the painting was taken to his country home at Chartwell but was not put on display. After the death of Lady Churchill in 1977, it became clear that she had destroyed the painting some months after it was delivered.
[7]
Churchill was an elder statesman in 1954, then towards the end of his second period as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. Sutherland had a reputation as a modernist painter with some recent successful portraits, such as Somerset Maugham in 1949. He was drawn to capturing the real person: some sitters considered his disinclination to flattery as a form of cruelty or disparagement.
[8]
The presentation ceremony at Westminster Hall was recorded by the BBC. In his acceptance speech, Churchill remarked on the unprecedented honour shown to him, and described the painting (in a remark often considered a backhanded compliment) as "a remarkable example of modern art", combining "force with candour". Other reactions were mixed, with some critics praising the strength of its likeness, but others condemned it as a disgrace.
The presentation ceremony at Westminster Hall was recorded by the BBC. In his acceptance speech, Churchill remarked on the unprecedented honour shown to him, and described the painting (in a remark often considered a backhanded compliment) as "a remarkable example of modern art", combining "force with candour". Other reactions were mixed, with some critics praising the strength of its likeness, but others condemned it as a disgrace.
[9]
There are more examples of portraits destroyed by the sitters who disliked it, for example the portrait of French playwright Alfred Jarry painted by Henri Rousseau. I am not aware if there are photographs of this work.
Neither of the portrait Lucian Freud made of Bernard Breslauer, a dealer in antique books. In the news, published by the Daily Telegraph in August 2008, we read that"The painting of Bernard Breslauer, a millionaire antiquarian book dealer, was finished more than 50 years ago and Freud was anxious for it to be included in the exhibition in London next month.
But after a long search Freud was devastated to discovered that the painting had been destroyed by Breslauer who took over the family business after his father died when their Bloomsbury flat was destroyed in the Blitz.
Mr Breslauer, apparently, objected to the way Freud had painted his distinctive double chin."
[10]
Although perhaps the best example in terms of destruction of portraits is the case of the American painter Thomas Eakins. As we read in the book of Henry Adams:
"Almost invariably, Eakins's portraits were poorly received. Four of Eakins's commisioned portraits were rejected. That of the President Rutherford Hayes were destroyed. In 1899 the colleagues of Dean James W. Holland objected to the dean's "tense almos haggard expression" and refused to pay for it. As Holland's son explained, Eakins, "having no general market at that time... as a friendly gesture gave the picture to my mother". In two cases, those of Robert Ogden and Atwater Lee, the sitters agreed to pay Eakins's fee, but never diplayed them; one returned the portrait to Eakins's studio.
Most often, Eakins would simply give the portraits he had painted to the sitter or the sitter's family, often with an accompanying inscription. Many never bothered to pick up their portraits. Others destroyed the gift. Eakins painted both James and George Wood, the sons of his physician Dr. Horatio C. Wood, but both portraits have disappeared. George wrote to Goodrich: "He painted a portrait of me was quite 'Eakineeze', so much so that my family got it lost". In 1903 Eakins gave a portrait of his former pupil, Frank W. Stokes, to his family, who destroyed it. The same fate met his portrait of the pugilist Charlie McKeever, which Eakins gave to the fighter's mother. John Singer Sargent (or his family) misplaced or destroyed the portrait that Eakins gave him of their mutual friend Dr. J. William White. Similary, the Buckley family destroyed the painting of Edward S. Buckley that Eakins painted in 1906. His daughter wrote: "It was so unsatisfactory that we destroyed it not wishing his descendants to think of their grandfather as resemblign such a portrait." Mary Waldon, the Superior of the Order of the Sisters of Mercy, did not like her portrait by Eakins and called in another painter, William Antrim, to paint one that was more pleasing. Antrim took the Eakins portrait off its stretcher and "tossed" in into the attic of his studio, where it was subsequently lost."